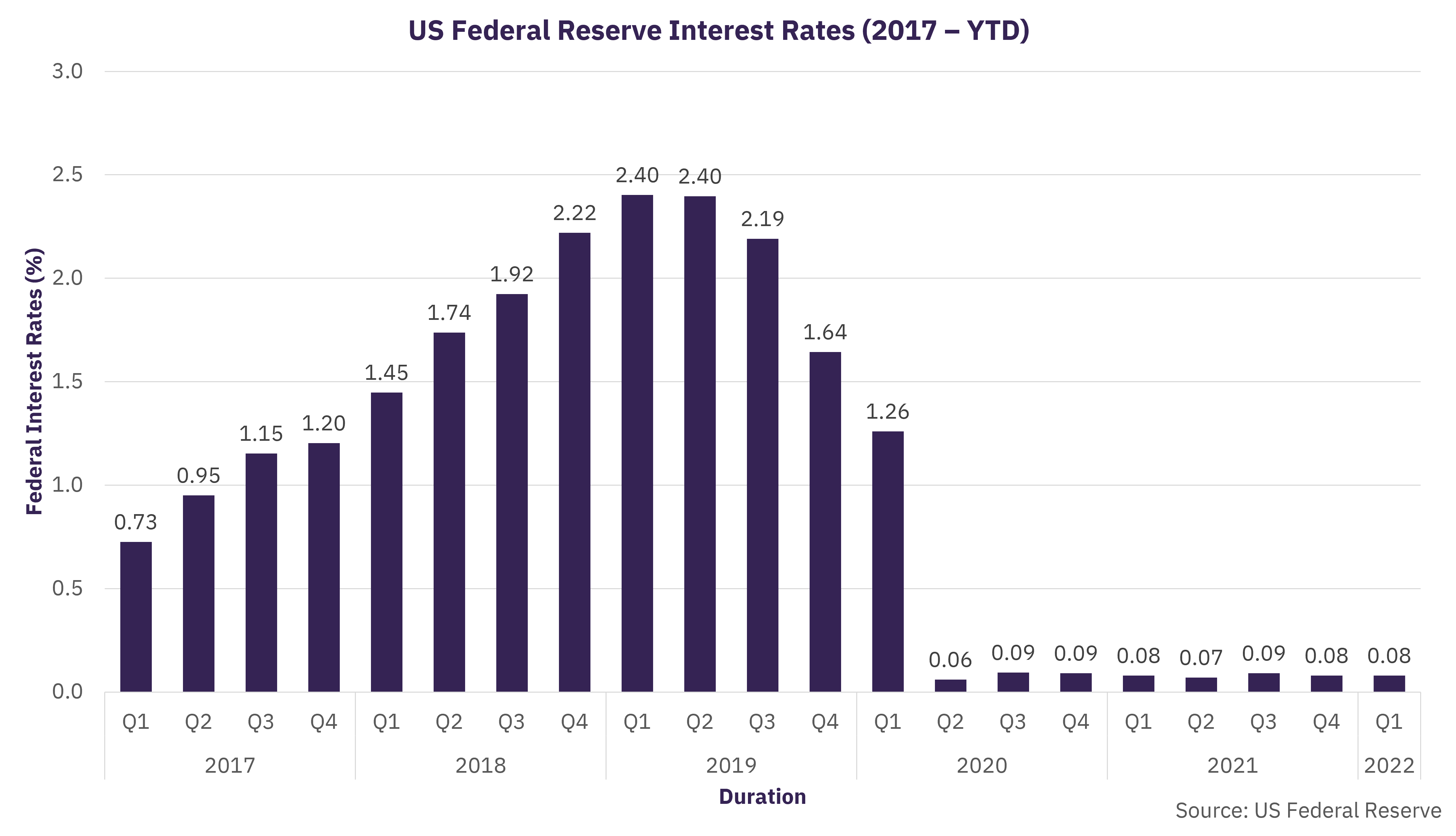
The Federal Reserve interest rates play a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of the United States. As the central bank of the nation, the Federal Reserve, often referred to as "the Fed," manages these rates to influence economic growth, employment, and inflation. Understanding how these rates function and their implications can provide valuable insights into the broader economic environment, affecting everything from mortgage rates to savings interest. Given their significance, it's no wonder these rates are closely monitored by economists, policymakers, and the general public alike.
The Federal Reserve uses interest rates as a tool to control the supply of money within the economy. By adjusting these rates, the Fed can either encourage borrowing and spending or promote savings and investment. This delicate balance aims to maintain economic stability and growth. The decision-making process involves a complex analysis of current economic conditions, including employment data, inflation rates, and global economic trends.
While the concept of interest rates might seem straightforward, the implications of changes in the Federal Reserve interest rates are far-reaching. They can impact not only national economic performance but also global market trends. As such, understanding the intricacies of these rates and their adjustments can provide a clearer picture of economic strategies and forecasts. This article will delve into the history, function, and effects of the Federal Reserve interest rates, offering an in-depth exploration for those eager to comprehend their importance in today's economic climate.
Read also:5movierulzkim Everything You Need To Know About This Popular Platform
Table of Contents
- The History of Federal Reserve Interest Rates
- How Do Federal Reserve Interest Rates Function?
- Impact of Federal Reserve Interest Rates on the Economy
- What is the Decision-Making Process Behind Federal Reserve Interest Rates?
- Factors That Influence Federal Reserve Interest Rates
- Federal Reserve Interest Rates: A Global Perspective
- How Do Federal Reserve Interest Rates Control Inflation?
- Ensuring Employment Stability Through Federal Reserve Interest Rates
- Impact on Investments and Savings
- How Do Federal Reserve Interest Rates Affect Mortgages and Loans?
- Future Predictions for Federal Reserve Interest Rates
- Public Perception and Reaction to Federal Reserve Interest Rates Changes
- Case Studies: Past Impacts of Federal Reserve Interest Rate Changes
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
The History of Federal Reserve Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve, established in 1913, has been pivotal in shaping the monetary policy of the United States. The interest rates set by the Fed have varied significantly over the decades, influenced by numerous economic events and trends. Initially, the Federal Reserve system was created to provide a stable and secure monetary framework to prevent financial panics, predominantly focusing on stabilizing the banking sector.
Throughout the 20th century, the Federal Reserve interest rates underwent numerous changes, reflecting the evolving economic conditions. The Great Depression of the 1930s saw a significant shift in monetary policy, as the Fed lowered interest rates to stimulate economic activity. Conversely, the inflationary pressures of the late 1970s and early 1980s led to a substantial increase in rates, aiming to curb inflation and stabilize the economy.
In more recent history, the financial crisis of 2008 prompted the Federal Reserve to implement near-zero interest rates to spur economic recovery. This period marked a significant turning point, as unconventional monetary policies, such as quantitative easing, were introduced to complement traditional interest rate adjustments. Understanding these historical shifts provides context for the current strategies employed by the Fed.
How Do Federal Reserve Interest Rates Function?
The Federal Reserve interest rates are a key instrument in the implementation of monetary policy. Primarily, the Fed manipulates the federal funds rate, which is the interest rate at which depository institutions lend balances to each other overnight. This rate serves as a benchmark for other interest rates in the economy, impacting everything from short-term loans to long-term mortgage rates.
When the Federal Reserve adjusts the federal funds rate, it influences the cost of borrowing money. A lower rate makes borrowing cheaper, encouraging businesses and consumers to take loans to invest and spend, thereby boosting economic activity. Conversely, a higher rate makes borrowing more expensive, prompting savings and reducing expenditure, which can help control inflation.
Moreover, the Federal Reserve uses various tools to ensure that the actual federal funds rate aligns with its target rate. These tools include open market operations, which involve the buying and selling of government securities, and the setting of reserve requirements for banks. By understanding these mechanisms, one can appreciate the complexity and precision involved in the Fed's management of interest rates.
Read also:5movierulz Tamil 2024 Your Goto Platform For Latest Tamil Movies
Impact of Federal Reserve Interest Rates on the Economy
The effects of Federal Reserve interest rates on the economy are profound and multifaceted. These rates influence economic growth, employment, consumer spending, and investment, among other factors. Consequently, changes in the federal funds rate can have wide-reaching implications for the broader economy.
One of the primary impacts of Federal Reserve interest rates is on consumer spending. Lower interest rates reduce the cost of borrowing, making loans for homes, cars, and other consumer goods more affordable. This increased accessibility can stimulate consumer demand and drive economic growth. Conversely, higher rates can dampen consumer spending by increasing borrowing costs, which can slow economic expansion.
The investment landscape is also affected by Federal Reserve interest rates. Lower rates typically lead to higher investment levels, as businesses find it cheaper to finance expansion projects and innovation initiatives. However, higher rates might discourage investment due to the increased cost of capital. These dynamics underline the critical role of interest rates in shaping the economic environment.
What is the Decision-Making Process Behind Federal Reserve Interest Rates?
The decision-making process for Federal Reserve interest rates is intricate and involves a comprehensive analysis of various economic indicators. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), comprising members of the Federal Reserve Board and regional Federal Reserve Bank presidents, meets regularly to assess current economic conditions and determine appropriate interest rate adjustments.
During these meetings, the FOMC evaluates a wide range of data, including employment figures, inflation rates, consumer spending, and global economic trends. This analysis helps the committee gauge the overall health of the economy and the potential risks it faces. Based on these assessments, the FOMC decides whether to raise, lower, or maintain the federal funds rate to achieve its dual mandate of maximum employment and price stability.
Additionally, the FOMC considers the potential long-term effects of interest rate changes, balancing the need for immediate economic support with the goal of sustainable growth. This careful deliberation ensures that the Federal Reserve's monetary policy remains effective and responsive to evolving economic conditions.
Factors That Influence Federal Reserve Interest Rates
Several factors influence the Federal Reserve's decisions on interest rates. A key consideration is the state of the economy, particularly regarding inflation and employment levels. The Fed closely monitors these indicators to determine whether the economy is operating at its full potential or if there are signs of overheating or recession.
Inflation is a critical factor in interest rate decisions. When inflation is high, the Federal Reserve may increase interest rates to cool economic activity and prevent prices from rising too quickly. Conversely, when inflation is low, the Fed might lower rates to stimulate spending and investment.
Employment levels also play a significant role in the Fed's decision-making process. The Federal Reserve aims to achieve maximum employment, so high unemployment rates might prompt the Fed to lower interest rates to encourage job creation. Conversely, if the labor market is too tight, the Fed might raise rates to prevent overheating.
Moreover, global economic conditions can influence Federal Reserve interest rate decisions. Events such as trade tensions, geopolitical instability, and international financial crises can affect the U.S. economy, prompting the Fed to adjust rates accordingly to mitigate potential risks.
Federal Reserve Interest Rates: A Global Perspective
The Federal Reserve interest rates have significant implications beyond the borders of the United States, influencing global economic trends and financial markets. As the world's largest economy, changes in U.S. interest rates can lead to shifts in international capital flows, exchange rates, and investment patterns.
When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it often leads to an appreciation of the U.S. dollar, making American exports more expensive and potentially affecting trade balances. Additionally, higher U.S. rates can attract foreign capital, leading to capital outflows from emerging markets and potential financial instability.
Conversely, when the Fed lowers interest rates, it can lead to a depreciation of the dollar, making U.S. exports more competitive and potentially benefiting the trade balance. Lower rates can also encourage capital inflows into emerging markets, boosting their economic growth prospects.
Given these global implications, the Federal Reserve closely monitors international economic developments when making interest rate decisions. This global perspective ensures that the Fed's monetary policy remains effective in a complex and interconnected world economy.
How Do Federal Reserve Interest Rates Control Inflation?
Federal Reserve interest rates are a vital tool for controlling inflation and maintaining price stability. By adjusting the federal funds rate, the Fed can influence the supply of money in the economy and, in turn, the overall price level of goods and services.
When inflation is high, the Federal Reserve may raise interest rates to reduce consumer and business spending. By making borrowing more expensive, higher rates can dampen demand and reduce upward pressure on prices. This approach helps prevent inflation from spiraling out of control and ensures that the economy remains stable.
Conversely, when inflation is low, the Fed might lower interest rates to encourage spending and investment. By making borrowing cheaper, lower rates can boost demand and help lift prices, preventing deflationary pressures that can harm economic growth.
This delicate balancing act is central to the Federal Reserve's mission of maintaining price stability while supporting economic growth. By effectively managing interest rates, the Fed can ensure that inflation remains within a target range, promoting a healthy and sustainable economic environment.
Ensuring Employment Stability Through Federal Reserve Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve interest rates play a critical role in ensuring employment stability and supporting job creation. By influencing borrowing costs and economic activity, the Fed can help maintain a balanced labor market and achieve its mandate of maximum employment.
When unemployment is high, the Federal Reserve may lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth and encourage businesses to hire more workers. By reducing the cost of borrowing, lower rates can boost investment and consumer spending, leading to increased demand for goods and services and, ultimately, more job opportunities.
Conversely, when the labor market is too tight, the Fed might raise interest rates to prevent overheating and control wage inflation. Higher rates can moderate economic activity and ensure that employment levels remain sustainable over the long term.
This focus on employment stability underscores the importance of Federal Reserve interest rates in shaping labor market dynamics and supporting the broader economy. By carefully managing these rates, the Fed can help ensure that Americans have access to job opportunities and that the economy remains resilient and vibrant.
Impact on Investments and Savings
Federal Reserve interest rates significantly impact investments and savings decisions, influencing the behavior of both individual investors and financial institutions. By affecting borrowing costs and the returns on savings, these rates play a crucial role in determining the allocation of capital within the economy.
Lower interest rates tend to boost investment by reducing the cost of financing projects and encouraging businesses to expand and innovate. As borrowing becomes cheaper, companies are more likely to undertake new ventures, leading to increased economic activity and job creation.
Conversely, higher interest rates can discourage investment by raising the cost of capital. Businesses may delay or scale back expansion plans when borrowing becomes more expensive, potentially slowing economic growth.
Interest rates also affect savings decisions. When rates are low, the return on savings accounts and fixed-income investments decreases, potentially discouraging savings and prompting individuals to seek higher-yielding alternatives, such as stocks or real estate. Conversely, higher rates can encourage savings by offering more attractive returns on deposits and fixed-income securities.
Understanding these dynamics is essential for investors and savers alike, as Federal Reserve interest rates can have a profound impact on financial planning and wealth accumulation strategies.
How Do Federal Reserve Interest Rates Affect Mortgages and Loans?
Federal Reserve interest rates have a direct impact on mortgages and loans, influencing the cost of borrowing for consumers and businesses. Changes in the federal funds rate can lead to fluctuations in mortgage rates, personal loans, and other forms of credit.
When the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates, mortgage rates typically decrease, making home loans more affordable for prospective buyers. This reduction in borrowing costs can stimulate the housing market, encouraging more people to purchase homes and invest in real estate.
Conversely, when the Fed raises interest rates, mortgage rates tend to increase, making home loans more expensive. This rise in borrowing costs can dampen demand for housing and potentially slow the real estate market.
Similarly, changes in Federal Reserve interest rates affect other types of loans, such as auto loans, student loans, and credit card rates. Lower rates can reduce the cost of borrowing for these types of credit, while higher rates can increase the financial burden on borrowers.
Understanding the relationship between Federal Reserve interest rates and mortgages and loans is crucial for consumers and businesses alike, as it can inform financial decisions and budgeting strategies.
Future Predictions for Federal Reserve Interest Rates
Predicting future Federal Reserve interest rates involves analyzing a wide range of economic indicators and understanding the Fed's monetary policy objectives. While exact forecasts are challenging, economists and analysts use various models and data to make informed predictions about the direction of interest rates.
Factors such as inflation trends, employment levels, and global economic conditions all play a role in shaping future interest rate decisions. The Federal Reserve's dual mandate of maximum employment and price stability guides its monetary policy, and any changes in these indicators can influence the Fed's approach to interest rates.
Additionally, external events such as geopolitical tensions, trade policies, and financial market dynamics can impact the Fed's interest rate decisions. As such, future predictions require a comprehensive understanding of both domestic and international economic developments.
While predicting the exact trajectory of Federal Reserve interest rates is complex, staying informed about economic trends and the Fed's policy objectives can help individuals and businesses anticipate potential changes and adapt their financial strategies accordingly.
Public Perception and Reaction to Federal Reserve Interest Rates Changes
Public perception and reaction to changes in Federal Reserve interest rates can significantly influence economic behavior and sentiment. The Fed's decisions are closely monitored by the media, financial markets, and the general public, often leading to widespread discussion and debate.
When the Federal Reserve announces interest rate changes, the public's reaction can vary depending on economic conditions and individual circumstances. Lower interest rates are generally perceived positively by consumers, as they reduce borrowing costs and make loans more affordable. This perception can boost consumer confidence and spending, supporting economic growth.
Conversely, higher interest rates may be viewed negatively by some consumers and businesses, as they increase borrowing costs and potentially slow economic activity. However, higher rates can also be seen as a sign of a strong economy, indicating that the Fed is confident in the economic outlook and is taking steps to control inflation.
Understanding public perception and reaction to interest rate changes is essential for policymakers and economists, as it can influence economic expectations and behavior. By effectively communicating their decisions and rationale, the Federal Reserve can help manage public sentiment and ensure that its policies remain effective and well-received.
Case Studies: Past Impacts of Federal Reserve Interest Rate Changes
Examining past impacts of Federal Reserve interest rate changes can provide valuable insights into the effects of monetary policy on the economy. Historical case studies highlight the diverse outcomes of interest rate adjustments and the factors that influence their effectiveness.
One notable case study is the interest rate hikes of the late 1970s and early 1980s, when the Federal Reserve raised rates to combat high inflation. This aggressive tightening of monetary policy successfully reduced inflation but also led to a recession and increased unemployment. The episode underscores the challenges of balancing inflation control with economic growth.
Another significant case study is the response to the 2008 financial crisis, when the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates to near zero to stimulate economic recovery. This period marked the introduction of unconventional monetary policies, such as quantitative easing, which helped stabilize financial markets and support economic growth.
These case studies illustrate the complex and multifaceted nature of Federal Reserve interest rate changes and their impacts on the economy. By analyzing past experiences, policymakers and economists can gain valuable insights into the potential effects of future interest rate decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Federal Reserve interest rates?
Federal Reserve interest rates refer to the rates set by the Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, which influence borrowing costs and economic activity. The most well-known rate is the federal funds rate, which affects other interest rates in the economy.
How do Federal Reserve interest rates affect inflation?
Federal Reserve interest rates control inflation by influencing the supply of money in the economy. Higher rates reduce spending and borrowing, helping to control inflation, while lower rates encourage spending and investment, potentially boosting inflation when it's low.
Why does the Federal Reserve change interest rates?
The Federal Reserve changes interest rates to achieve its dual mandate of maximum employment and price stability. Adjusting rates helps the Fed manage economic growth, control inflation, and support job creation.
How do interest rate changes affect mortgages?
Interest rate changes impact mortgages by influencing the cost of borrowing. Lower Federal Reserve rates typically lead to reduced mortgage rates, making home loans more affordable, while higher rates can increase borrowing costs and slow the housing market.
What factors influence Federal Reserve interest rate decisions?
Factors influencing Federal Reserve interest rate decisions include inflation, employment levels, economic growth, and global economic conditions. The Fed analyzes these indicators to determine the appropriate rate adjustments to achieve its policy objectives.
How are Federal Reserve interest rates set?
Federal Reserve interest rates are set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which meets regularly to assess economic conditions and determine rate adjustments. The committee evaluates various economic indicators to guide its decisions.
Conclusion
Federal Reserve interest rates are a vital component of the United States' monetary policy, influencing economic growth, inflation, employment, and financial markets. Understanding the intricacies of these rates and their implications can provide valuable insights into the broader economic environment.
As the Federal Reserve continues to navigate the complexities of the modern economy, its interest rate decisions will remain a focal point for policymakers, economists, and the public alike. By staying informed about the factors that influence these rates and their potential impacts, individuals and businesses can better anticipate changes and adapt their financial strategies accordingly.
The dynamic nature of the global economy ensures that Federal Reserve interest rates will continue to be a critical tool for maintaining economic stability and promoting sustainable growth. As such, ongoing analysis and discussion of these rates and their effects will remain essential for understanding the evolving economic landscape.