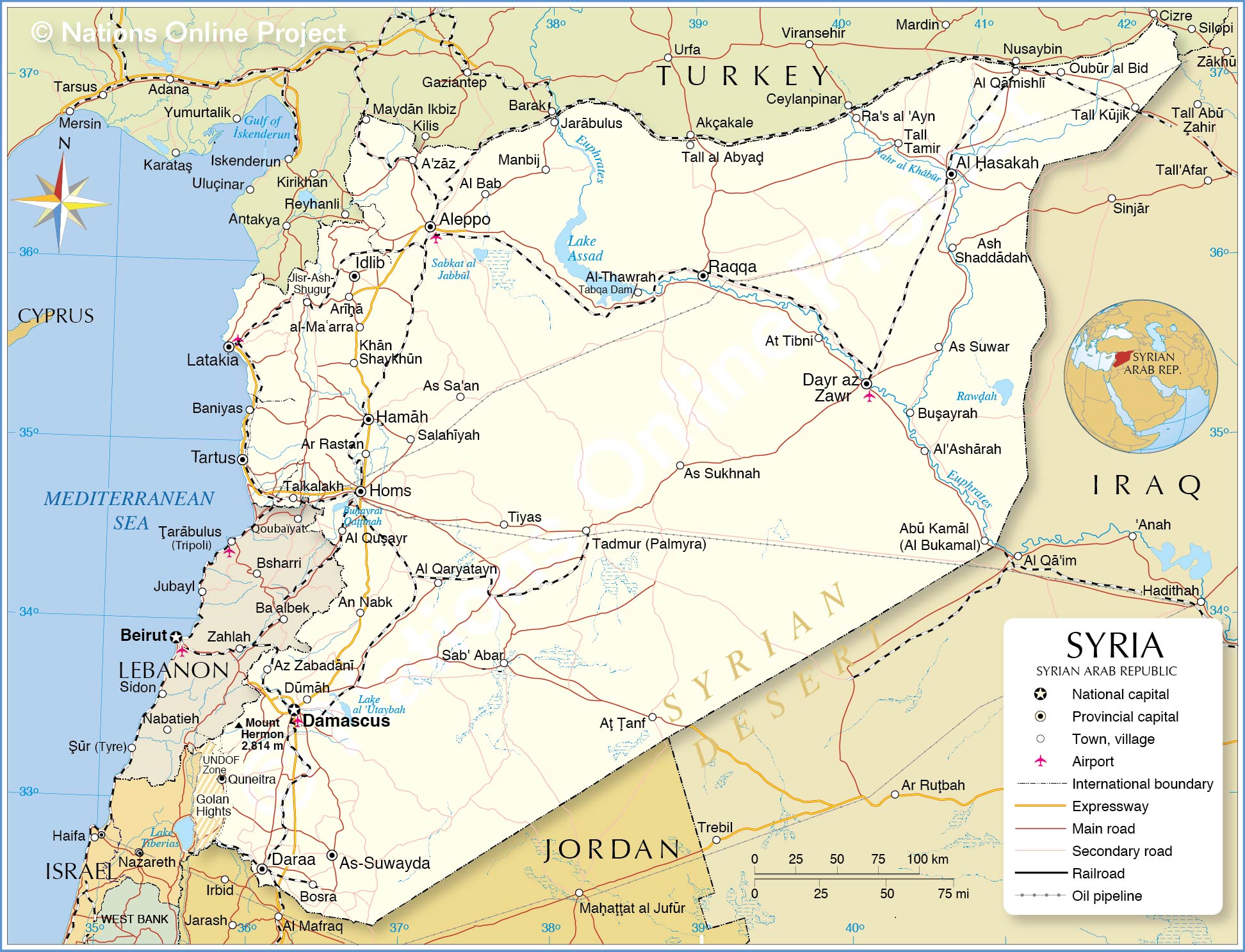
The complexities of Syria extend beyond its borders. Its cultural heritage is a testament to the many empires that have ruled the region, including the Romans, Byzantines, and Ottomans. This cultural mosaic is reflected in the country's architecture, language, and customs. However, Syria's modern challenges are rooted in political, social, and economic upheavals that have led to widespread displacement and suffering. As we delve into the intricacies of Syria's past and present, it becomes clear that understanding this nation requires a nuanced approach. By exploring its history, culture, economy, and international relations, we can gain a deeper appreciation for Syria's role on the world stage and the enduring spirit of its people.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Location | Middle East |
| Capital | Damascus |
| Official Language | Arabic |
| Population | Approx. 17 million (2021) |
| Currency | Syrian Pound (SYP) |
Table of Contents
- Historical Background of Syria
- What is Syria's Cultural Heritage?
- Geopolitical Significance of Syria
- How is Syria's Economic Landscape Shaped?
- Impact of the Civil War on Syria
- The Humanitarian Crisis in Syria
- Syria's International Relations
- Future Prospects for Syria
- Historical Background of Syria
- What is Syria's Cultural Heritage?
- Geopolitical Significance of Syria
- How is Syria's Economic Landscape Shaped?
- Impact of the Civil War on Syria
- The Humanitarian Crisis in Syria
- Syria's International Relations
- Future Prospects for Syria
- FAQs about Syria
- Conclusion
Historical Background of Syria
Syria's history is a tapestry woven with the threads of ancient civilizations and empires. Situated in a region often referred to as the cradle of civilization, Syria has been home to some of the world's earliest settlements. The city of Damascus, its capital, is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities globally, with a history dating back to the 3rd millennium BCE.
The ancient city of Ebla, located in modern-day Syria, was a significant center in the third millennium BCE. It played a pivotal role in trade and diplomacy in the ancient Near East. Subsequently, Syria became part of various empires, including the Akkadian, Babylonian, and Assyrian empires. Each of these empires left an indelible mark on the region’s history and culture.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Hd Movie Hub 4u Your Gateway To Highquality Entertainment
During the Roman and Byzantine periods, Syria flourished as a province known for its prosperity and urbanization. The city of Palmyra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, stands as a testament to this era. Palmyra was a vital trade center that connected the Roman Empire with the Persian and Indian worlds.
The advent of Islam in the 7th century marked a new chapter in Syria's history. Damascus became the capital of the Umayyad Caliphate, which was the first major Islamic dynasty. The Umayyad Mosque in Damascus remains one of the oldest and largest mosques in the world, showcasing the architectural brilliance of the era.
In the succeeding centuries, Syria witnessed the rise and fall of several Islamic dynasties, including the Abbasids, Ayyubids, and Mamluks. Each dynasty contributed to the region's cultural and architectural heritage. The Ottoman Empire's annexation of Syria in the 16th century brought relative stability and integration into a vast empire that spanned three continents.
The early 20th century saw the end of Ottoman rule, leading to the French mandate period. This era laid the groundwork for modern Syrian nationalism and the eventual independence of Syria in 1946. The post-independence period was marked by political instability, coups, and eventually the establishment of the Ba'ath Party's rule under Hafez al-Assad in 1970.
Syria's recent history has been shaped significantly by the Assad family, with Hafez al-Assad's son, Bashar al-Assad, assuming power in 2000. The Assad regime has been characterized by authoritarian rule, and the current civil war, which began in 2011, has plunged the country into a protracted conflict with far-reaching consequences.
What is Syria's Cultural Heritage?
Syria's cultural heritage is a rich mosaic reflecting its diverse historical influences. Archaeological sites, ancient ruins, and architectural marvels showcase the country's storied past. Syria's cultural heritage is not only a testament to its history but also a vital component of its national identity.
Read also:Telugu Latest Movies Trends Highlights And Mustwatch Films
One of the most iconic symbols of Syria's cultural heritage is the city of Aleppo. Known for its ancient citadel and bustling souks, Aleppo has been a center of commerce and culture for centuries. Unfortunately, the ongoing conflict has taken a toll on the city's historical fabric, with significant damage to many of its heritage sites.
The ancient city of Palmyra, once a thriving trade hub, is another jewel of Syria's cultural heritage. The ruins of Palmyra, including its temples, colonnaded streets, and the iconic Arch of Triumph, offer a glimpse into the grandeur of the past. However, the conflict has also impacted Palmyra, with several monuments suffering damage and destruction.
Syria is home to six UNESCO World Heritage Sites, including the Ancient City of Damascus, the Ancient City of Bosra, and the Crac des Chevaliers. These sites are invaluable for understanding the region's history and cultural evolution. The preservation and restoration of these sites are crucial for future generations and the promotion of cultural tourism.
The country's cultural diversity is also reflected in its traditions, music, and cuisine. Syrian cuisine is renowned for its rich flavors and use of fresh ingredients. Dishes like kibbeh, tabbouleh, and baklava are enjoyed by Syrians and people worldwide. Traditional music, with its unique blend of Arabic, Turkish, and Persian influences, continues to be an integral part of Syrian culture.
The vibrant cultural tapestry of Syria is also evident in its festivals and celebrations. From religious festivals like Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha to cultural events like the Damascus International Film Festival, these occasions showcase the country's artistic and cultural dynamism.
Syria's cultural heritage is not only about its past but also its present and future. Efforts to preserve and restore cultural sites are underway, despite the challenges posed by the ongoing conflict. Organizations and individuals are working tirelessly to safeguard Syria's cultural legacy for future generations.
Geopolitical Significance of Syria
Syria's geopolitical significance is primarily attributed to its strategic location in the Middle East, bordered by Turkey, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, and Israel. Its proximity to major political and economic centers makes it a crucial player in regional dynamics and international relations.
The Syrian landscape is a complex mosaic of ethnic and religious groups, including Arabs, Kurds, Alawites, Sunnis, Christians, and Druze. This diversity has historically shaped Syria's internal politics and external relations. The country's geopolitical importance is further underscored by its role as a transit hub for energy resources, particularly oil and gas pipelines.
Syria's geopolitical significance has often placed it at the center of regional conflicts and power struggles. The Cold War era saw Syria aligning with the Soviet Union, which provided military and economic support. This alignment influenced Syria's foreign policy and its role in the Arab-Israeli conflict.
The ongoing civil war in Syria has drawn the attention of major global and regional powers, each with vested interests in the outcome. The conflict has become a proxy war, with countries like Russia, Iran, the United States, Turkey, and Saudi Arabia supporting different factions. This involvement has complicated the conflict and prolonged the humanitarian crisis.
Syria's geopolitical significance is also linked to its role in regional security dynamics. The country is a key player in the fight against extremist groups like ISIS, which have exploited the chaos of the civil war to establish a presence in the region. Syria's stability is crucial for maintaining regional security and preventing the spread of extremism.
The future of Syria's geopolitical significance will depend on the resolution of the ongoing conflict and the establishment of a stable and inclusive political system. Regional and international cooperation is essential for achieving a lasting peace and addressing the underlying causes of the conflict.
Syria's role in the broader Middle East and its relations with neighboring countries will continue to shape its geopolitical significance. As the country navigates its challenges, its strategic location and diverse population will remain central to its regional and global interactions.
How is Syria's Economic Landscape Shaped?
The economic landscape of Syria has been profoundly impacted by years of conflict, sanctions, and political instability. Before the onset of the civil war, Syria had a diverse economy with sectors such as agriculture, industry, and services contributing to its GDP.
Agriculture has traditionally been a vital sector for Syria, employing a significant portion of the population. The fertile plains of the Euphrates River have supported the cultivation of crops like wheat, cotton, and barley. However, the conflict has disrupted agricultural production, leading to food insecurity and loss of livelihoods.
The industrial sector in Syria, including oil production and manufacturing, has also suffered due to the war. The destruction of infrastructure, loss of skilled labor, and sanctions have severely hampered industrial output. The oil sector, once a major source of revenue, has been particularly affected by the conflict and international sanctions.
The service sector, which encompasses banking, tourism, and trade, has also faced significant challenges. The tourism industry, once a growing contributor to the economy, has been devastated by the conflict, with many historical sites and tourist destinations becoming inaccessible.
Despite these challenges, Syria's economic landscape has shown resilience in certain areas. The informal economy has expanded, with small businesses and entrepreneurs finding ways to adapt to the difficult circumstances. Local markets and trade networks have persisted, providing essential goods and services to the population.
The reconstruction of Syria's economy will require significant investment and international cooperation. Rebuilding infrastructure, revitalizing agriculture, and revitalizing the industrial sector are essential for economic recovery. The lifting of sanctions and the establishment of a stable political environment will also be crucial for attracting foreign investment and fostering economic growth.
Syria's economic future will depend on the implementation of comprehensive economic reforms that address the structural challenges and promote sustainable development. These reforms should focus on diversifying the economy, improving governance, and enhancing social welfare to ensure inclusive growth and stability.
Impact of the Civil War on Syria
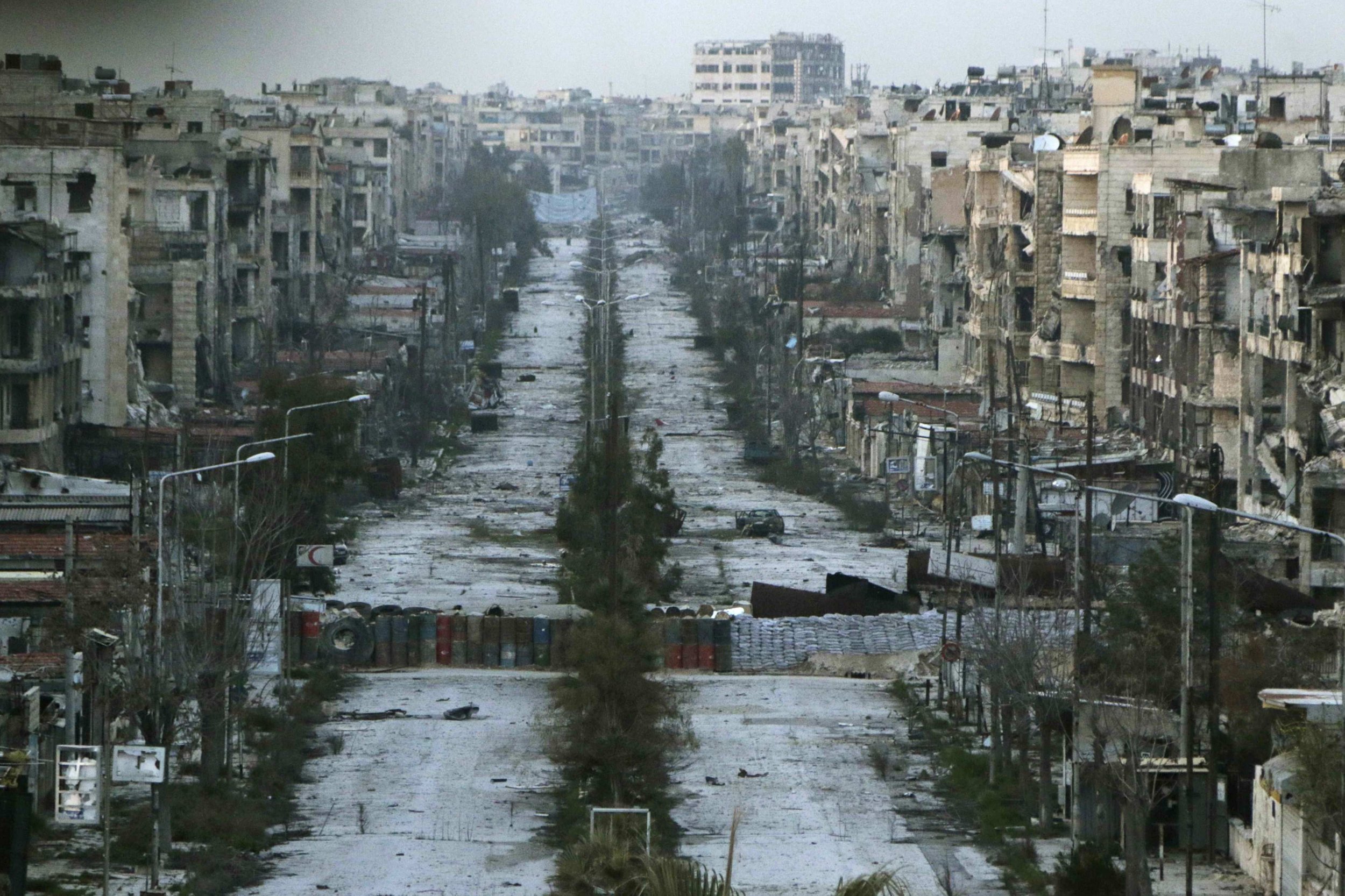
The civil war in Syria, which began in 2011, has had a devastating impact on the country and its people. The conflict has resulted in widespread destruction, loss of life, and displacement, with millions of Syrians forced to flee their homes.
The humanitarian impact of the civil war is staggering. The United Nations estimates that over 13 million people in Syria are in need of humanitarian assistance, with millions facing food insecurity and limited access to healthcare and education. The conflict has also led to the internal displacement of millions of Syrians and the creation of a large refugee population in neighboring countries and beyond.
The civil war has also had a profound impact on Syria's infrastructure and economy. The destruction of cities, towns, and villages has resulted in a severe loss of housing, schools, hospitals, and other essential facilities. The conflict has disrupted economic activities, leading to unemployment, poverty, and a decline in living standards.
The social fabric of Syrian society has been deeply affected by the conflict, with divisions along ethnic, religious, and political lines exacerbated by the violence. The war has also resulted in widespread human rights abuses, including torture, arbitrary detention, and the use of chemical weapons.
The international community has been engaged in efforts to address the humanitarian crisis and support efforts to achieve a peaceful resolution to the conflict. However, the complex nature of the conflict and the involvement of multiple external actors have made progress difficult.
Despite the challenges, there are signs of hope for Syria's future. Efforts to rebuild and rehabilitate affected areas are underway, with local communities and international organizations working together to provide essential services and support livelihoods. The resilience and determination of the Syrian people are crucial for overcoming the challenges and building a peaceful and prosperous future.
The impact of the civil war on Syria will be felt for generations to come. Addressing the humanitarian, economic, and social consequences of the conflict will require sustained efforts and a commitment to peace and reconciliation.
The Humanitarian Crisis in Syria
The humanitarian crisis in Syria is one of the most severe in the world, with millions of people affected by the ongoing conflict. The crisis is characterized by widespread displacement, food insecurity, lack of healthcare, and limited access to education and other essential services.
The conflict has displaced millions of Syrians both internally and externally, with many seeking refuge in neighboring countries such as Turkey, Lebanon, and Jordan. The refugee crisis has placed significant strain on host communities and exacerbated regional tensions.
Food insecurity is a major concern in Syria, with many families struggling to access affordable and nutritious food. The conflict has disrupted agricultural production and supply chains, leading to rising food prices and limited availability of essential goods.
The healthcare system in Syria has been severely affected by the conflict, with many hospitals and clinics damaged or destroyed. Access to healthcare is limited, and there is a shortage of medical supplies and personnel. The situation is particularly dire for vulnerable groups such as children, the elderly, and those with chronic illnesses.
Education has also been disrupted, with many schools damaged or used as shelters for displaced families. Thousands of children have been denied the opportunity to attend school, impacting their future prospects and development.
International humanitarian organizations and local NGOs are working tirelessly to provide assistance to those in need. Efforts to deliver food, medical care, and other essential services are ongoing, but challenges such as insecurity and access restrictions hinder the response.
Addressing the humanitarian crisis in Syria requires a comprehensive approach that includes providing immediate relief, supporting long-term recovery, and promoting peace and stability. The international community must continue to support humanitarian efforts and work towards a peaceful resolution to the conflict.
Syria's International Relations
Syria's international relations are characterized by its strategic location and complex geopolitical dynamics. The country's foreign policy and international interactions have been shaped by its historical alliances, regional rivalries, and the ongoing civil war.
Historically, Syria has maintained close ties with Russia and Iran, which have provided political, military, and economic support. These alliances have been crucial for the Assad regime, particularly during the civil war, where both countries have played significant roles in supporting the government.
Syria's relations with its Arab neighbors have been influenced by the broader regional context, including the Arab-Israeli conflict and the dynamics of the Arab League. The civil war has strained Syria's relations with several Arab countries, with some supporting opposition groups and others backing the government.
The involvement of the United States and other Western countries in the Syrian conflict has further complicated Syria's international relations. The imposition of sanctions and diplomatic isolation by Western countries has impacted Syria's economy and international standing.
The ongoing conflict has also affected Syria's relations with Turkey, which has been involved in military operations along its border with Syria and has hosted a large number of Syrian refugees. The complex dynamics between Syria and Turkey have implications for regional stability and security.
Syria's international relations are further influenced by its role in regional security dynamics, particularly in relation to extremist groups and the fight against terrorism. The country's stability is crucial for regional security, and international cooperation is essential for addressing security challenges.
Despite the challenges, Syria's international relations hold the potential for positive change. Diplomatic efforts to resolve the conflict and rebuild Syria's international standing are underway. Engaging with regional and global actors and fostering dialogue will be crucial for Syria's future and its role on the world stage.
Future Prospects for Syria
The future prospects for Syria are shaped by the country's ongoing challenges and the potential for peace and stability. The resolution of the civil war, economic recovery, and the rebuilding of social and political institutions are essential for Syria's future.
The peace process in Syria remains a complex and ongoing effort, with various international actors and stakeholders involved. Achieving a lasting and inclusive peace will require addressing the root causes of the conflict, promoting reconciliation, and establishing a political system that represents all Syrians.
Economic recovery is a critical component of Syria's future prospects. Rebuilding infrastructure, revitalizing agriculture and industry, and attracting investment will be essential for restoring the economy and improving living standards. International support and cooperation will be crucial for economic recovery and development.
The social fabric of Syria will also need to be rebuilt, with efforts to promote social cohesion, address grievances, and support the return of displaced populations. Education, healthcare, and social services must be prioritized to ensure the well-being and development of the population.
Syria's future prospects are also linked to regional and international dynamics. The country's role in regional security, its relations with neighboring countries, and its position in the global community will shape its future interactions and development.
Despite the challenges, there is hope for Syria's future. The resilience and determination of the Syrian people, combined with international support and cooperation, can pave the way for a peaceful and prosperous future. Building a stable, inclusive, and thriving Syria will require sustained efforts and a commitment to peace and development.
FAQs about Syria
- What is the current population of Syria?
The current population of Syria is estimated to be around 17 million, although this figure is constantly changing due to displacement and migration.
- What languages are spoken in Syria?
The official language of Syria is Arabic. However, Kurdish, Armenian, and Assyrian are also spoken by minority communities.
- What are the major religions in Syria?
Syria is religiously diverse, with Islam being the predominant religion. The majority of Muslims are Sunni, but there are also significant Alawite, Shia, and Christian communities.
- How has the civil war affected Syria's economy?
The civil war has severely impacted Syria's economy, leading to the destruction of infrastructure, disruption of economic activities, and loss of livelihoods. Sanctions and the conflict have also affected the oil and industrial sectors.
- What efforts are being made to preserve Syria's cultural heritage?
Efforts to preserve Syria's cultural heritage include restoration and rehabilitation projects, documentation of heritage sites, and international cooperation to protect cultural property. Organizations like UNESCO are actively involved in these efforts.
- What is the status of the peace process in Syria?
The peace process in Syria is ongoing, with various international actors and stakeholders involved. Efforts to achieve a lasting and inclusive peace continue, but challenges remain in addressing the root causes of the conflict and promoting reconciliation.
Conclusion
Syria's story is one of resilience and complexity, marked by a rich historical legacy, cultural diversity, and modern challenges. Understanding the intricate dynamics of Syria requires a comprehensive approach that considers its historical context, cultural heritage, geopolitical significance, and the impact of the civil war.
The humanitarian crisis in Syria remains a pressing concern, requiring sustained international support and cooperation. Efforts to provide relief, promote peace, and rebuild the country are essential for addressing the challenges faced by the Syrian people.
The future prospects for Syria hold the potential for positive change, with opportunities for peace, economic recovery, and social cohesion. The resilience and determination of the Syrian people, combined with international efforts, can pave the way for a peaceful and prosperous future.
Syria's journey is a testament to the enduring spirit of its people and the importance of international solidarity in addressing complex challenges. As we look to the future, the hope for a stable, inclusive, and thriving Syria remains a shared aspiration for all.