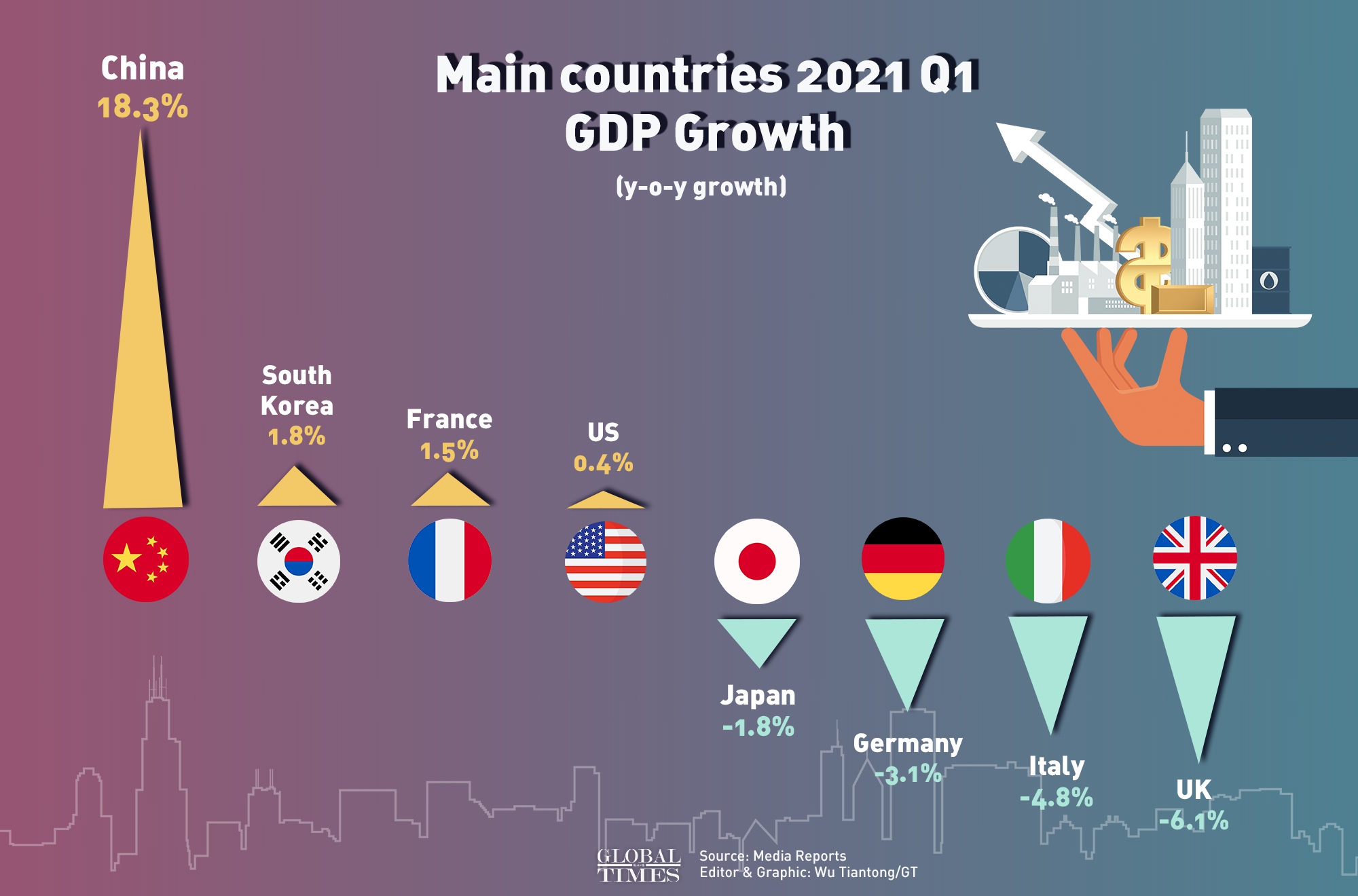
Gross Domestic Product, or GDP, is a critical measure used worldwide to gauge the economic performance of countries. It serves as a comprehensive scorecard of a nation’s economic health, encapsulating the total value of goods and services produced over a specific time period. Understanding GDP is essential for government policymakers, economists, investors, and even the general public, as it influences economic strategies, monetary policies, and investment decisions.
GDP not only provides insights into the economic progress of a country but also allows for comparisons between different economies. By measuring GDP, countries can assess whether their economies are growing, stagnating, or declining, which in turn helps them make informed decisions about spending, taxation, and other economic policies. It reflects the economic activities within a country’s borders and is typically measured annually or quarterly, offering a snapshot of economic productivity.
While GDP is a powerful tool, it is not without its limitations. Critics argue that it does not account for the distribution of income among residents of a country, nor does it consider whether the nation's rate of growth is sustainable in the long term. Moreover, GDP does not measure the informal economy or non-market transactions, such as volunteer work and household labor. Despite these limitations, GDP remains an invaluable indicator of economic health and a primary focus of economic analysis worldwide.
Read also:Masafun Online Your Ultimate Guide To A Unique Digital Experience
Table of Contents
- What is GDP?
- History of GDP
- Components of GDP
- How is GDP Calculated?
- Nominal vs Real GDP
- GDP and Economic Growth
- GDP and the Global Economy
- Limitations of GDP
- How Does GDP Affect You?
- GDP and Investment Decisions
- GDP and International Trade
- GDP in Developing Countries
- Future of GDP
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
What is GDP?
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a monetary measure representing the market value of all final goods and services produced in a period (quarterly or yearly) within a country's borders. It serves as a comprehensive indicator of a nation's economic activity and is often used to compare the economic performance of different countries.
History of GDP
The concept of GDP was developed in the early 20th century by economist Simon Kuznets. Initially presented to the U.S. Congress in 1934 during the Great Depression, GDP provided a way to measure economic performance. Over the years, it has evolved to become a global standard for economic assessment.
Components of GDP
GDP is composed of four main components: consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports (exports minus imports). Each component reflects different aspects of economic activity:
- Consumption: Spending by households on goods and services.
- Investment: Spending on capital goods that will be used for future production.
- Government Spending: Expenditures by government on goods and services.
- Net Exports: The value of a country's exports minus its imports.
How is GDP Calculated?
GDP can be calculated using three approaches: the production approach, the income approach, and the expenditure approach. Each approach provides a different perspective on economic activity but should, in theory, yield the same GDP figure.
- Production Approach: Calculates GDP by adding up the value of all goods and services produced.
- Income Approach: Measures GDP by summing all incomes earned in the production of goods and services.
- Expenditure Approach: Adds up total spending on the nation's final goods and services.
Nominal vs Real GDP
Nominal GDP measures a country's economic output using current prices, without adjusting for inflation. Real GDP, on the other hand, is adjusted for inflation, providing a more accurate reflection of an economy's size and how it's growing over time. Real GDP allows for comparisons across years, showing true economic growth.
GDP and Economic Growth
GDP is a crucial indicator of economic growth, showing how much a country’s economy is expanding. An increase in GDP typically signifies a growing economy, while a decrease might indicate economic troubles. Policymakers and economists closely monitor GDP trends to guide economic policy and decision-making.
Read also:Everything You Need To Know About Www 5movierulz 2023 Telugu
GDP and the Global Economy
GDP plays a significant role in the global economy, influencing international trade, investment, and economic policies. Countries with high GDPs are often seen as more stable and attractive for investment, while those with lower GDPs may struggle to attract foreign capital.
Limitations of GDP
Despite its widespread use, GDP has several limitations. It does not account for income inequality, environmental degradation, or non-market transactions. GDP also does not measure the informal economy and can sometimes give a skewed view of economic health.
How Does GDP Affect You?
GDP affects individuals in various ways. As an indicator of economic health, it influences employment rates, income levels, and government policy. A growing GDP generally means more job opportunities and higher wages, while a declining GDP can lead to unemployment and lower income.
GDP and Investment Decisions
Investors use GDP data to make informed decisions about where to allocate resources. A strong GDP growth rate might indicate a healthy economy and potential investment opportunities, while a declining GDP could signal economic issues and risks.
GDP and International Trade
GDP is closely linked to international trade, as it affects a country's trade balance and competitiveness. A higher GDP can lead to increased exports, while a lower GDP might signify less competitive production capacity.
GDP in Developing Countries
In developing countries, GDP is used to measure economic progress and development. However, it may not fully capture the informal economy, which can be a significant part of these economies. Policymakers in developing nations use GDP to craft strategies for growth and poverty reduction.
Future of GDP
The future of GDP as an economic measure is evolving. Some economists advocate for alternative measures that incorporate well-being and sustainability, such as the Human Development Index (HDI) or Gross National Happiness (GNH). These alternative metrics aim to provide a more holistic view of economic and social progress.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What does GDP stand for? GDP stands for Gross Domestic Product.
- How often is GDP measured? GDP is typically measured quarterly and annually.
- Why is GDP important? GDP is important because it indicates the economic health of a country and informs policy decisions.
- What is the difference between nominal and real GDP? Nominal GDP uses current prices, while real GDP is adjusted for inflation.
- Can GDP measure well-being? GDP does not directly measure well-being, as it focuses on economic output without considering social factors.
- How does GDP affect exchange rates? A strong GDP can lead to a stronger currency, influencing exchange rates.
Conclusion
GDP remains a vital tool for understanding economic performance and guiding policy decisions. While it is not without its limitations, it provides a valuable snapshot of economic activity and growth. As the global economy evolves, alternative measures may complement GDP, offering a more nuanced view of economic and social progress.
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)