Understanding the implications of "poor hygiene" is essential in maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Poor hygiene can be described as the neglect of basic cleanliness practices that are crucial for personal health and the well-being of others in the community. This can include inadequate washing of hands, irregular bathing, and insufficient oral care, among other activities. The consequences of poor hygiene can manifest in various forms, ranging from minor inconveniences to severe health issues and societal implications.
When individuals fail to adhere to basic hygiene practices, they inadvertently expose themselves and others to a myriad of health risks. These risks can include bacterial, viral, and fungal infections, which can spread rapidly in communities with inadequate hygiene standards. Furthermore, poor hygiene is often linked with social stigmatization, as individuals may be perceived as unkempt or unsanitary, potentially impacting their social interactions and opportunities.
The importance of understanding the "poor hygiene meaning" extends beyond personal health; it encompasses a broader societal perspective. Hygiene practices are foundational to public health initiatives worldwide, aiming to reduce the spread of diseases and improve overall quality of life. By highlighting the significance of proper hygiene, we can foster healthier communities and encourage individuals to adopt and maintain effective hygiene practices.
Read also:Unlocking The Sui Meaning A Deep Dive Into Its Essence
Table of Contents
- Definition of Poor Hygiene
- Historical Perspective on Hygiene Practices
- Common Consequences of Poor Hygiene
- How Does Poor Hygiene Affect Health?
- Psychological Impacts of Poor Hygiene
- Social Implications of Poor Hygiene
- Preventive Measures for Better Hygiene
- Importance of Education in Promoting Hygiene
- Global Hygiene Standards and Initiatives
- Technology and Innovations in Hygiene
- How Can Poor Hygiene Affect the Economy?
- Role of Government in Hygiene Promotion
- Cultural Differences in Hygiene Practices
- Future Trends in Hygiene Awareness
- FAQs about Poor Hygiene
Definition of Poor Hygiene
Poor hygiene refers to the failure to maintain cleanliness and grooming practices that are necessary for good health and well-being. It encompasses neglecting actions such as regular handwashing, bathing, dental care, and maintaining clean living conditions. Poor hygiene can lead to the accumulation of dirt, bacteria, and other harmful pathogens on the body and in the environment, increasing the risk of diseases.
Several factors contribute to poor hygiene, including lack of awareness, access to hygiene products, cultural beliefs, and personal habits. Poor hygiene is not only a personal concern but also a public health issue, as it can facilitate the spread of infectious diseases and contribute to outbreaks.
Historical Perspective on Hygiene Practices
Throughout history, hygiene practices have evolved significantly, influenced by cultural, technological, and scientific advancements. In ancient civilizations, hygiene was often linked to religious or spiritual rituals. For example, the Egyptians were known for their use of perfumes and oils for cleanliness and spiritual purposes.
The Roman Empire emphasized public baths and sanitation systems, recognizing the importance of cleanliness in urban environments. However, during the Middle Ages, hygiene standards declined, leading to widespread diseases and plagues. The Renaissance and Enlightenment periods saw renewed interest in hygiene, with the introduction of soaps and medical advancements that highlighted the connection between cleanliness and health.
Key Developments in Hygiene Over the Centuries
- Ancient Egyptian use of oils and perfumes for cleanliness.
- Roman public baths and sophisticated sanitation systems.
- Decline in hygiene during the Middle Ages, contributing to disease spread.
- Renaissance advancements in soap production and medical hygiene.
- 19th-century public health movements emphasizing sanitation.
Common Consequences of Poor Hygiene
Poor hygiene can lead to a wide range of health and social consequences. These include:
- Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections due to the accumulation of pathogens.
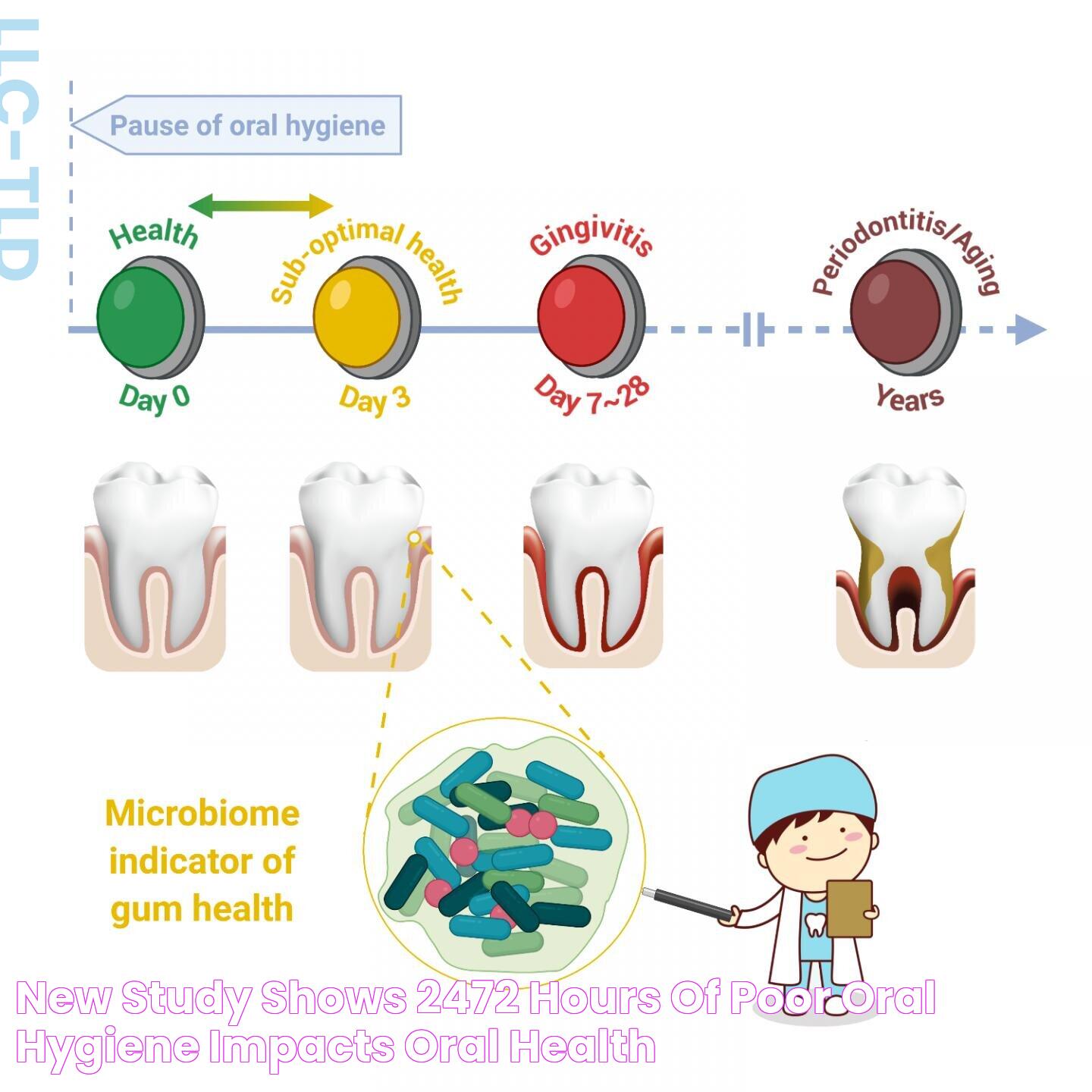
- Dental problems such as cavities and gum disease from inadequate oral care.
- Skin conditions like acne, rashes, and infections from lack of cleanliness.
- Social isolation and stigmatization due to perceived uncleanliness.
- Increased absenteeism from school or work due to hygiene-related illnesses.
Infections and Diseases Linked to Poor Hygiene
Numerous infections are directly linked to poor hygiene practices, including:
Read also:All About Voldemort Nose A Comprehensive Analysis
- Gastrointestinal infections from contaminated hands or food.
- Respiratory infections spread through unwashed hands.
- Skin and soft tissue infections due to lack of washing and grooming.
How Does Poor Hygiene Affect Health?
Poor hygiene significantly impacts physical health by increasing the susceptibility to infections and diseases. The skin, as the body's largest organ, acts as the first line of defense against pathogens. Without proper hygiene, the skin can become a breeding ground for bacteria and fungi, leading to skin infections and other health issues.
Oral health is also affected by poor hygiene. Neglecting dental care can result in plaque buildup, cavities, and gum disease, which can have further health implications if left untreated. Additionally, poor hygiene can compromise the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to illnesses and reducing the ability to fight off infections.
Long-Term Health Implications
Chronic poor hygiene can lead to long-term health problems, including:
- Compounded dental issues leading to tooth loss and systemic infections.
- Persistent skin conditions that can result in scarring or secondary infections.
- Increased risk of serious diseases due to weakened immune defense.
Psychological Impacts of Poor Hygiene
Poor hygiene can have profound psychological effects, contributing to diminished self-esteem and confidence. Individuals with poor hygiene may experience embarrassment and social anxiety, fearing judgment or rejection from peers. This can lead to a cycle of social withdrawal and isolation, exacerbating mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
Moreover, poor hygiene in childhood can impact social development, as children may face bullying or exclusion due to their appearance or smell. Addressing hygiene issues can improve mental well-being, fostering better social interactions and a positive self-image.
Strategies for Overcoming Psychological Barriers
Overcoming the psychological impacts of poor hygiene involves:
- Building awareness and education on the importance of hygiene.
- Encouraging open discussions about personal hygiene without judgment.
- Providing access to hygiene resources and support systems.
Social Implications of Poor Hygiene
Poor hygiene extends beyond personal health, affecting social dynamics and interactions. Individuals with poor hygiene may face social stigmatization, impacting their ability to form relationships and participate in community activities. In workplaces or schools, poor hygiene can lead to discrimination or exclusion, affecting productivity and performance.
Furthermore, poor hygiene can strain healthcare systems, as preventable diseases spread more easily in communities with inadequate hygiene practices. Public health initiatives often emphasize the importance of hygiene education and resources to address these social implications.
Building Community Awareness and Support
Communities can tackle the social implications of poor hygiene by:
- Implementing community hygiene education programs.
- Providing access to hygiene facilities and supplies.
- Encouraging community involvement in hygiene promotion activities.
Preventive Measures for Better Hygiene
Improving hygiene requires adopting preventive measures that promote cleanliness and health. Key practices include:
- Regular handwashing with soap and water to remove germs.
- Frequent bathing and grooming to maintain skin and hair health.
- Consistent oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing.
- Maintaining clean and sanitary living environments.
- Using sanitary products and following safe food handling practices.
Educating individuals and communities on these practices is crucial in fostering better hygiene habits and reducing the spread of diseases.
Role of Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns play a vital role in promoting hygiene by:
- Raising awareness about the benefits of good hygiene practices.
- Providing resources and support for hygiene education.
- Encouraging community participation in hygiene improvement initiatives.
Importance of Education in Promoting Hygiene
Education is a fundamental component in promoting good hygiene practices. Schools and community programs can provide valuable information on the importance of hygiene and its impact on health and well-being. By integrating hygiene education into curriculums, children can learn about proper hygiene practices from an early age, fostering lifelong habits.
In addition, adult education programs can address cultural and societal barriers to hygiene, encouraging individuals to adopt healthier practices. Tailoring educational materials to specific communities can ensure that hygiene messages are relevant and impactful.
Effective Educational Strategies
To effectively promote hygiene education, strategies should include:
- Interactive workshops and demonstrations on hygiene practices.
- Distribution of educational materials and resources.
- Incorporating hygiene topics into broader health education programs.
Global Hygiene Standards and Initiatives
Global hygiene standards are established to ensure consistent and effective hygiene practices worldwide. Organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF work to promote hygiene through international guidelines and initiatives. These efforts aim to improve access to hygiene resources, reduce the spread of infectious diseases, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals and communities.
Key global initiatives focus on providing clean water, sanitation facilities, and hygiene education, particularly in underserved regions. By collaborating with local governments and organizations, these initiatives strive to build sustainable hygiene solutions that cater to diverse cultural and environmental needs.
Notable Global Hygiene Initiatives
Some notable global hygiene initiatives include:
- WHO's Global Handwashing Day to promote handwashing awareness.
- UNICEF's WASH (Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene) program for improved hygiene access.
- Partnerships with NGOs to implement community-based hygiene projects.
Technology and Innovations in Hygiene
Advancements in technology have revolutionized hygiene practices, making them more efficient and accessible. Innovations such as smart hygiene devices, antimicrobial materials, and digital health platforms have enhanced personal and public hygiene standards.
Smart devices, including touchless faucets and soap dispensers, reduce the risk of cross-contamination, while antimicrobial coatings on surfaces and textiles help prevent the spread of pathogens. Digital platforms provide hygiene education and resources, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their hygiene practices.
Emerging Technologies in Hygiene
Emerging technologies that are transforming hygiene include:
- AI-powered hygiene monitoring systems for public spaces.
- Wearable devices that track and promote personal hygiene habits.
- Innovative water purification and sanitation solutions.
How Can Poor Hygiene Affect the Economy?
Poor hygiene can have substantial economic implications, affecting productivity and healthcare costs. In workplaces, hygiene-related illnesses can lead to increased absenteeism, reduced efficiency, and higher healthcare expenses. Industries reliant on hygiene, such as food production and healthcare, face significant risks from poor hygiene practices, which can result in financial losses and reputational damage.
Furthermore, poor hygiene can hinder economic development in communities with limited access to hygiene resources. Investing in hygiene infrastructure and education can stimulate economic growth by improving public health and reducing disease burdens.
Economic Benefits of Improved Hygiene
Investing in hygiene can yield several economic benefits, including:
- Increased workforce productivity and reduced absenteeism.
- Lower healthcare costs due to fewer hygiene-related illnesses.
- Enhanced reputation and compliance in hygiene-dependent industries.
Role of Government in Hygiene Promotion
Governments play a crucial role in promoting hygiene through policy-making, resource allocation, and public health initiatives. By implementing regulations and standards, governments can ensure that hygiene practices are upheld across various sectors, including food safety, healthcare, and education.
Government-funded programs and campaigns can raise awareness about the importance of hygiene and provide necessary resources and support to communities. Collaborating with international organizations and NGOs can further enhance the reach and effectiveness of hygiene promotion efforts.
Government Strategies for Hygiene Promotion
Effective government strategies for promoting hygiene include:
- Developing national hygiene policies and standards.
- Funding public health campaigns and education programs.
- Facilitating access to hygiene facilities and resources.
Cultural Differences in Hygiene Practices
Hygiene practices can vary significantly across cultures, influenced by traditions, beliefs, and environmental factors. Understanding these cultural differences is essential in promoting effective hygiene practices that respect and align with local customs.
For example, some cultures emphasize particular grooming rituals or dietary practices that impact hygiene. By recognizing and incorporating these cultural elements into hygiene education and initiatives, programs can achieve greater acceptance and success in diverse communities.
Adapting Hygiene Practices to Cultural Contexts
Adapting hygiene practices to cultural contexts involves:
- Engaging with community leaders to understand local practices.
- Incorporating traditional hygiene methods into modern practices.
- Respecting cultural beliefs while promoting hygiene benefits.
Future Trends in Hygiene Awareness
As global awareness of hygiene continues to grow, several trends are emerging that will shape the future of hygiene practices. These include increased emphasis on sustainability, personalized hygiene solutions, and the integration of technology in hygiene education and resources.
Sustainability efforts focus on reducing waste and environmental impact associated with hygiene products and practices. Personalized hygiene solutions cater to individual needs and preferences, enhancing the effectiveness and adoption of hygiene practices. The integration of technology, such as virtual reality and mobile applications, enhances hygiene education and accessibility, reaching broader audiences.
Key Trends Shaping the Future of Hygiene
Key trends in the future of hygiene include:
- Development of eco-friendly and sustainable hygiene products.
- Customized hygiene solutions for diverse populations.
- Use of digital tools to enhance hygiene education and engagement.
FAQs about Poor Hygiene
What is poor hygiene?
Poor hygiene refers to the neglect of maintaining cleanliness and grooming habits necessary for good health. This includes infrequent handwashing, bathing, and oral care, as well as maintaining clean living environments.
How does poor hygiene affect health?
Poor hygiene can lead to health issues such as infections, skin conditions, and dental problems. It also weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses.
Can poor hygiene impact mental health?
Yes, poor hygiene can affect mental health by contributing to low self-esteem, social anxiety, and depression due to perceived uncleanliness and social stigmatization.
What are some common signs of poor hygiene?
Common signs of poor hygiene include body odor, unkempt appearance, dental issues, and skin problems. It may also manifest in unclean living environments.
How can poor hygiene be improved?
Improving poor hygiene involves adopting regular cleaning and grooming habits, such as frequent handwashing, bathing, and oral care, as well as maintaining clean environments.
Why is hygiene education important?
Hygiene education is vital as it raises awareness about the importance of cleanliness and its impact on health. It empowers individuals to adopt effective hygiene practices, reducing disease spread and improving quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding the "poor hygiene meaning" and its implications is crucial for promoting health and well-being. By addressing hygiene at personal, community, and global levels, we can reduce the spread of diseases, enhance social interactions, and improve overall quality of life. Through education, technology, and collaborative efforts, we can foster a future where good hygiene is accessible and practiced by all, contributing to healthier communities and a better world.
For further reading on global hygiene initiatives, visit UNICEF's WASH Program.