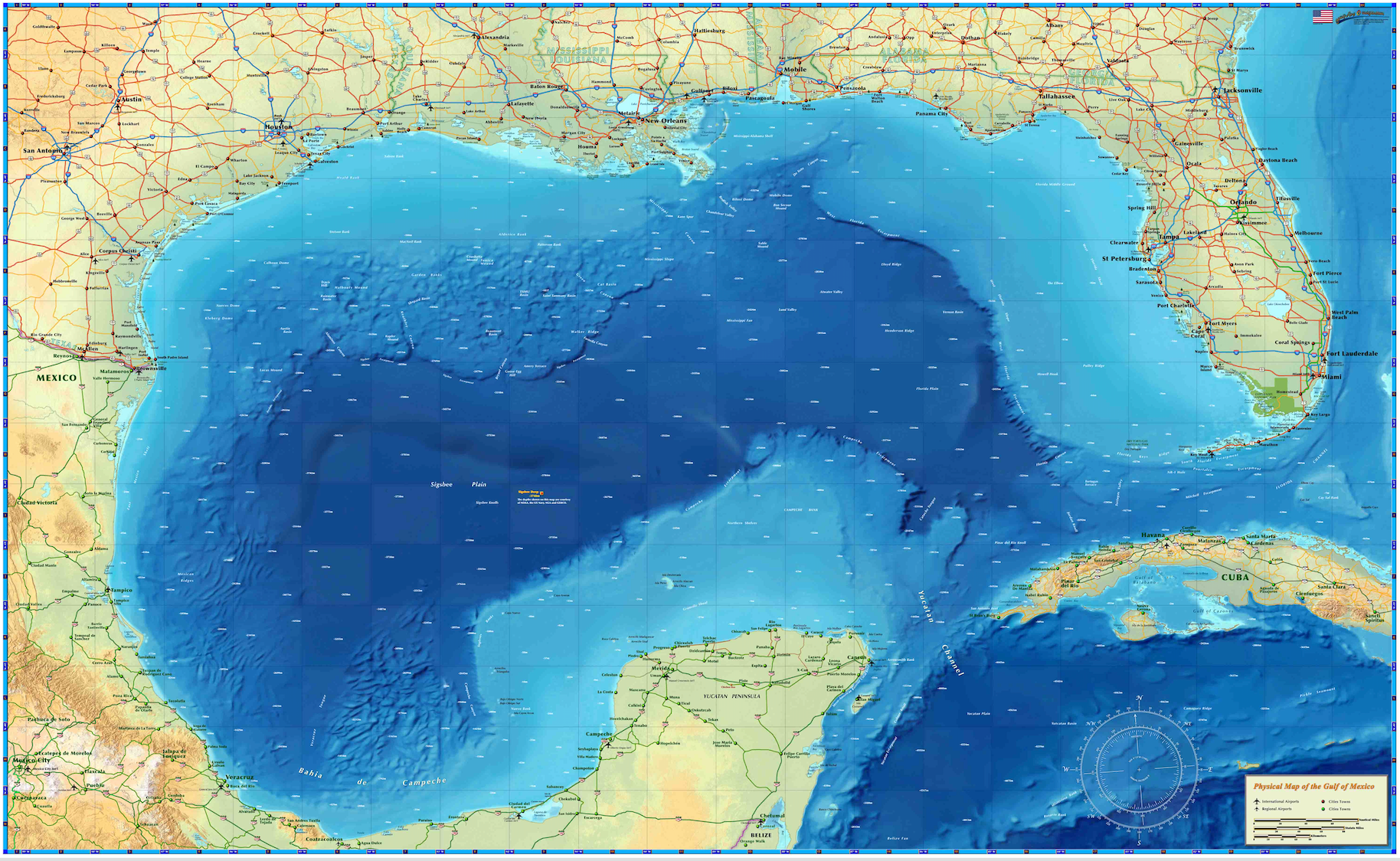
The Gulf of Mexico is a vast expanse of water bordered by the United States, Mexico, and Cuba, playing a pivotal role in the region's economy, culture, and environment. It is a uniquely diverse ecosystem, home to a wide variety of marine life, including dolphins, sea turtles, and countless fish species. The Gulf's rich biodiversity and natural resources have made it an area of significant interest for scientists, environmentalists, and policymakers alike.
Historically, the Gulf of Mexico has been a crucial hub for trade and commerce, providing a vital link between the North American continent and the rest of the world. With major ports like New Orleans, Houston, and Tampa Bay, the Gulf supports an array of industries, including shipping, fishing, and tourism. Its vast oil reserves make it a critical player in the energy sector, impacting global markets and local economies significantly.
However, the Gulf of Mexico is not without its challenges. Environmental concerns, such as oil spills, hurricanes, and the effects of climate change, threaten its delicate ecosystems and the livelihoods of those who depend on them. Conservation efforts and sustainable practices are more important than ever to preserve this natural wonder for future generations. This article delves into the various aspects of the Gulf of Mexico, exploring its natural beauty, economic significance, and the pressing issues it faces today.
Read also:Everything You Need To Know About Movie Ruls5 A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Geography and Formation of the Gulf of Mexico
- What Makes the Gulf of Mexico's Ecosystem Unique?
- Economic Impact of the Gulf of Mexico
- Cultural Significance of the Gulf of Mexico
- Historical Perspective on the Gulf of Mexico
- Oil and Energy in the Gulf of Mexico
- Fishing and Aquaculture in the Gulf of Mexico
- Shipping and Commerce in the Gulf of Mexico
- Tourism and Travel in the Gulf of Mexico
- Environmental Challenges Facing the Gulf of Mexico
- Conservation Efforts in the Gulf of Mexico
- Future Prospects for the Gulf of Mexico
- How Does the Gulf of Mexico Affect Climate?
- The Gulf of Mexico and Natural Disasters: What You Need to Know
- Conclusion
Geography and Formation of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is one of the world's largest bodies of water, covering an area of approximately 600,000 square miles. It is bordered by the southeastern United States to the north, Mexico to the west and south, and the island of Cuba to the southeast. The Gulf is a semi-enclosed sea, connected to the Atlantic Ocean through the Florida Straits and to the Caribbean Sea via the Yucatán Channel.
The formation of the Gulf of Mexico dates back to the Mesozoic era, around 300 million years ago, when the supercontinent Pangaea began to break apart. As tectonic plates shifted, a basin was created, eventually filling with water to form the Gulf. The Gulf's unique geological features, such as its continental shelf and deep-sea areas, contribute to its diverse marine environments.
Significant geographical features within the Gulf include the Mississippi River Delta, which deposits vast amounts of sediment, creating fertile grounds for marine life. The Loop Current, a warm ocean current that flows northward into the Gulf, plays a crucial role in regulating the region's climate and weather patterns.
What Makes the Gulf of Mexico's Ecosystem Unique?
The Gulf of Mexico boasts an incredibly diverse ecosystem, ranging from its coastal marshes and estuaries to its deep-sea environments. This diversity is due in part to the Gulf's unique geographical features and its warm, nutrient-rich waters. The Gulf is home to over 15,000 species of marine life, including fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and marine mammals.
Key habitats within the Gulf include coral reefs, seagrass beds, and mangrove forests. These ecosystems provide essential services, such as serving as breeding grounds for fish, protecting coastlines from erosion, and supporting a wide array of wildlife. The Gulf's coral reefs, particularly those found off the coast of Florida, are among the most biodiverse in the world, hosting hundreds of fish species and other marine organisms.
However, the Gulf's ecosystems are under threat from human activities, such as overfishing, pollution, and habitat destruction. Efforts to conserve and protect these vital habitats are crucial to maintaining the Gulf's ecological balance and ensuring the survival of its many species.
Read also:Mastering Efficiency The Ultimate Guide To 5move Rulz
Economic Impact of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a significant economic driver for the region, contributing billions of dollars annually to the economies of the United States, Mexico, and Cuba. Several key industries rely on the Gulf's resources, including oil and gas, fishing, shipping, and tourism.
Oil and gas extraction is perhaps the most well-known industry associated with the Gulf. The region is home to vast oil reserves, with thousands of offshore platforms extracting millions of barrels of oil each year. The Gulf's oil production plays a crucial role in supplying energy to North America and beyond, impacting global markets and economies.
Fishing is another vital industry in the Gulf, with thousands of commercial and recreational fishermen relying on its waters for their livelihoods. The Gulf is one of the most productive fishing areas in the world, supplying a significant portion of the United States' seafood, including shrimp, oysters, and various fish species.
The Gulf's ports, such as those in Houston, New Orleans, and Mobile, are essential hubs for shipping and commerce, facilitating the movement of goods between North and South America, Europe, and Asia. The region's tourism industry also thrives, with millions of visitors flocking to its beaches, resorts, and cultural attractions each year.
Cultural Significance of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico has long been a vital part of the cultural fabric of the communities that surround it. Its waters and shores have provided sustenance, transportation, and inspiration for countless generations, shaping the region's history and identity.
Many indigenous peoples, including the Maya and the Aztecs, relied on the Gulf's resources for food, trade, and transportation. The Gulf's rich natural environment supported complex societies, with thriving agricultural, fishing, and trading networks.
In more recent history, the Gulf has played a crucial role in the development of the United States and Mexico, serving as a gateway for exploration, colonization, and commerce. The region's ports facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures, contributing to the diverse and vibrant communities that exist today.
Today, the Gulf of Mexico continues to be a source of cultural pride and identity for the people who call its shores home. From the Cajun and Creole cultures of Louisiana to the vibrant music and art scenes of Florida and Texas, the Gulf's influence is evident in the region's rich cultural tapestry.
Historical Perspective on the Gulf of Mexico
The history of the Gulf of Mexico is a tapestry of exploration, conquest, and development, woven through the centuries by various civilizations. From ancient indigenous cultures to European explorers and modern industrialists, the Gulf has been a focal point for human activity and progress.
Before the arrival of Europeans, the Gulf was home to numerous indigenous peoples who harnessed its resources for sustenance and trade. The Maya, Aztecs, and other civilizations developed complex societies along its shores, leaving behind a legacy of art, architecture, and knowledge.
The arrival of European explorers in the 16th century marked a new era for the Gulf of Mexico. Spanish explorers, such as Hernán Cortés and Pánfilo de Narváez, ventured into the region, seeking wealth and new territories. Their expeditions laid the groundwork for Spanish colonization, which would shape the cultural and political landscape of the Gulf for centuries.
In the 19th and 20th centuries, the Gulf of Mexico emerged as a critical player in the global economy. The discovery of oil reserves transformed the region into a center of industry and innovation, driving economic growth and development. This period also saw the expansion of shipping, fishing, and tourism, further solidifying the Gulf's importance on the world stage.
Oil and Energy in the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a powerhouse for the oil and gas industry, with its vast reserves playing a critical role in meeting global energy demands. The region is home to thousands of offshore oil platforms, extracting millions of barrels of oil and cubic feet of natural gas each year.
The history of oil exploration in the Gulf dates back to the early 20th century, when the first offshore wells were drilled. Since then, advances in technology and engineering have allowed for the development of deeper and more complex fields, making the Gulf one of the most productive oil-producing regions in the world.
The impact of the oil and gas industry on the Gulf's economy cannot be overstated. It supports thousands of jobs, generates billions in revenue, and contributes significantly to the energy needs of North America and beyond. However, the industry also presents environmental challenges, such as oil spills and habitat destruction, which require careful management and regulation.
Fishing and Aquaculture in the Gulf of Mexico
Fishing and aquaculture are vital components of the Gulf of Mexico's economy and culture, providing food, income, and recreation for millions of people. The Gulf is one of the most productive fishing areas in the world, supporting a diverse array of species, including shrimp, oysters, and various fish.
Commercial fishing in the Gulf is a major industry, with thousands of fishermen and processors relying on its waters for their livelihoods. The region's seafood, particularly shrimp and oysters, is highly sought after both domestically and internationally, contributing significantly to the United States' seafood supply.
Recreational fishing is also a popular pastime in the Gulf, attracting anglers from around the world to its abundant waters. The Gulf's diverse marine life and scenic beauty make it a prime destination for sport fishing, supporting a thriving tourism industry.
However, the Gulf's fisheries face challenges from overfishing, habitat loss, and pollution. Sustainable management practices and conservation efforts are essential to ensuring the long-term health and productivity of the Gulf's marine resources.
Shipping and Commerce in the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a critical hub for shipping and commerce, facilitating the movement of goods between North and South America, Europe, and Asia. Its strategic location and extensive port infrastructure make it an essential component of global trade networks.
The Gulf's major ports, such as Houston, New Orleans, and Mobile, handle millions of tons of cargo each year, ranging from oil and gas to agricultural products and manufactured goods. These ports support thousands of jobs and generate billions in economic activity, making them vital to the region's economy.
In addition to its role in global trade, the Gulf's shipping industry also supports a range of related sectors, including shipbuilding, logistics, and transportation. The region's extensive network of waterways and transportation infrastructure further enhances its appeal as a center for commerce and industry.
However, the Gulf's shipping industry also faces challenges from environmental concerns, such as oil spills and habitat destruction. Efforts to balance economic growth with environmental protection are crucial to ensuring the long-term sustainability of the Gulf's commerce and trade.
Tourism and Travel in the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a popular destination for tourists from around the world, drawn to its beautiful beaches, vibrant culture, and diverse attractions. The region's tourism industry is a major economic driver, supporting thousands of jobs and generating billions in revenue each year.
Some of the Gulf's most popular destinations include the Florida Panhandle, the Texas Gulf Coast, and the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. These areas offer a wide range of attractions, from world-class beaches and resorts to cultural landmarks and natural wonders.
In addition to its natural beauty, the Gulf's rich cultural heritage also attracts visitors. The region is home to a diverse array of cultures and traditions, from the Cajun and Creole communities of Louisiana to the vibrant music and art scenes of Florida and Texas.
However, the Gulf's tourism industry also faces challenges from environmental concerns, such as hurricanes and oil spills. Efforts to promote sustainable tourism and protect the region's natural and cultural resources are essential to ensuring the long-term viability of the Gulf's tourism sector.
Environmental Challenges Facing the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico faces numerous environmental challenges, many of which are the result of human activities. These challenges threaten the delicate ecosystems and the livelihoods of those who depend on them, making conservation efforts more critical than ever.
One of the most significant environmental challenges facing the Gulf is pollution. Oil spills, such as the Deepwater Horizon disaster in 2010, have had devastating effects on the region's marine life and coastal communities. Additionally, agricultural runoff and industrial waste contribute to the Gulf's "dead zone," an area with low oxygen levels that cannot support most marine life.
Climate change is another pressing issue, with rising temperatures and sea levels threatening the Gulf's ecosystems and communities. The increasing frequency and intensity of hurricanes and other natural disasters further exacerbate these challenges, causing widespread damage and disruption.
Efforts to address these environmental challenges are crucial to preserving the Gulf's natural beauty and resources. Conservation initiatives, sustainable management practices, and international cooperation are all essential components of a comprehensive strategy to protect the Gulf for future generations.
Conservation Efforts in the Gulf of Mexico
Conservation efforts in the Gulf of Mexico are essential to preserving its unique ecosystems and ensuring the long-term sustainability of its resources. These efforts involve collaboration between governments, organizations, and individuals, all working together to protect the Gulf's natural beauty and biodiversity.
One of the key conservation initiatives in the Gulf is the restoration of coastal habitats, such as wetlands, mangroves, and seagrass beds. These habitats provide essential services, such as protecting coastlines from erosion, supporting marine life, and improving water quality.
Efforts to reduce pollution and improve water quality are also critical components of conservation in the Gulf. Initiatives to reduce agricultural runoff, improve wastewater treatment, and prevent oil spills are all essential to protecting the region's delicate ecosystems.
International cooperation is also crucial to conservation efforts in the Gulf, as its waters and resources are shared by multiple countries. Collaborative initiatives, such as the Gulf of Mexico Alliance, work to address shared challenges and promote sustainable management practices across the region.
Future Prospects for the Gulf of Mexico
The future prospects for the Gulf of Mexico are both promising and challenging, as the region continues to grapple with environmental issues, economic development, and cultural preservation. Balancing these competing interests is essential to ensuring the Gulf's long-term sustainability and prosperity.
One of the most promising aspects of the Gulf's future is the potential for sustainable economic growth. By adopting environmentally friendly practices and technologies, industries such as oil and gas, fishing, and tourism can continue to thrive while minimizing their impact on the region's ecosystems.
Advances in science and technology also hold promise for the Gulf's future, offering new tools and methods for addressing environmental challenges and improving resource management. Innovations in renewable energy, habitat restoration, and pollution control are all potential game-changers for the region.
However, the Gulf's future also depends on continued cooperation and collaboration between governments, organizations, and communities. By working together to address shared challenges and promote sustainable development, the Gulf's stakeholders can ensure a bright and prosperous future for the region.
How Does the Gulf of Mexico Affect Climate?
The Gulf of Mexico plays a significant role in influencing the climate of the surrounding regions, particularly in the southeastern United States. Its warm waters and unique geographical features contribute to various weather patterns and climatic conditions.
One of the most notable ways the Gulf affects climate is through its influence on hurricane activity. The warm waters of the Gulf provide the energy needed for these powerful storms to form and intensify. As a result, the Gulf Coast is particularly vulnerable to hurricanes, which can cause widespread damage and disruption.
The Gulf also plays a crucial role in regulating temperatures and precipitation patterns across the southeastern United States. The warm waters help to moderate temperatures, preventing extreme cold in the winter and reducing heat in the summer. Additionally, the Gulf's moisture contributes to precipitation patterns, influencing rainfall and weather systems in the region.
Overall, the Gulf of Mexico's impact on climate is a critical factor in understanding the region's weather patterns and preparing for future challenges. By studying the Gulf's influence on climate, scientists and policymakers can develop strategies to mitigate the effects of climate change and improve resilience in the face of natural disasters.
The Gulf of Mexico and Natural Disasters: What You Need to Know
The Gulf of Mexico is no stranger to natural disasters, with hurricanes, floods, and oil spills posing significant threats to the region's ecosystems and communities. Understanding the risks and impacts of these disasters is essential to developing effective strategies for mitigation and recovery.
Hurricanes are perhaps the most well-known natural disasters affecting the Gulf, with their powerful winds and storm surges causing widespread damage and disruption. The warm waters of the Gulf provide the energy needed for these storms to form and intensify, making the region particularly vulnerable to their impacts.
Flooding is another significant risk in the Gulf, especially during the hurricane season. Heavy rainfall and storm surges can lead to coastal and inland flooding, causing damage to infrastructure, homes, and ecosystems.
Oil spills, such as the Deepwater Horizon disaster, also pose significant environmental and economic challenges for the Gulf. These incidents can have devastating impacts on marine life, coastal habitats, and local economies, requiring extensive cleanup efforts and long-term recovery strategies.
Efforts to improve disaster preparedness and response are essential to mitigating the impacts of natural disasters in the Gulf. By investing in infrastructure, technology, and community resilience, the region can better withstand the challenges posed by these events.
Conclusion
The Gulf of Mexico is a region of immense beauty, diversity, and significance, with its waters and resources playing a crucial role in the lives of millions of people. From its rich ecosystems and vibrant cultures to its vital economic industries and pressing environmental challenges, the Gulf is a complex and dynamic region that demands our attention and care.
By understanding the Gulf's history, geography, and current challenges, we can work together to protect and preserve this vital resource for future generations. Through sustainable practices, conservation efforts, and international cooperation, we can ensure that the Gulf of Mexico continues to thrive and support the communities and ecosystems that depend on it.
FAQs
What is the significance of the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is significant due to its rich biodiversity, economic importance, and cultural influence. It is a critical hub for industries such as oil and gas, fishing, shipping, and tourism, contributing significantly to the region's economy and supporting millions of livelihoods.
How does the Gulf of Mexico impact the environment?
The Gulf of Mexico impacts the environment through its diverse ecosystems, which support a wide array of marine life and provide essential services such as protecting coastlines and improving water quality. However, human activities and environmental challenges, such as pollution and climate change, threaten these ecosystems.
What are the main economic activities in the Gulf of Mexico?
The main economic activities in the Gulf of Mexico include oil and gas extraction, fishing, shipping, and tourism. These industries contribute billions of dollars to the regional economy and support thousands of jobs.
How does the Gulf of Mexico influence climate?
The Gulf of Mexico influences climate by affecting weather patterns and precipitation in the southeastern United States. Its warm waters provide energy for hurricanes and moderate temperatures, impacting the region's climate and weather systems.
What are the major environmental challenges facing the Gulf of Mexico?
The major environmental challenges facing the Gulf of Mexico include pollution, habitat loss, overfishing, and the impacts of climate change. Addressing these challenges requires conservation efforts, sustainable management practices, and international cooperation.
How can we protect the Gulf of Mexico for future generations?
Protecting the Gulf of Mexico for future generations involves implementing sustainable practices, promoting conservation efforts, and fostering international cooperation. By addressing environmental challenges and balancing economic growth with ecological preservation, we can ensure the Gulf's long-term sustainability and prosperity.